prokaryotes plants palm tree drawings
Bacteria can thrive in a variety of environments, both extreme and normal in soil and water where most other species are found. Their ability to adapt to a variety of habitats underscores why bacteria, especially prokaryotes, are the most abundant organisms on Earth.
Difference between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit in every organism. Cells are of two different types namely prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. Organisms of the domains Bacteria and Archaea consist of prokaryotic cells. While organisms from the Eukarya domain such as protists, fungi, animals, and plants consist of eukaryotic cells.
Prokaryotes
Prokaryotes are characterized by not having a true nucleus with a cell membrane. the nucleus is actually free in the cell. The group of prokaryotes does not have mitochondrial cells and only has small ribosomes. In addition, prokaryotes do not have chloroplast cells. The groups that fall into the prokaryote group are bacteria and archaea. The cell wall in bacteria contains peptidoglycan or a peptidoglycan-like polymer, and does not contain chitin or cellulose. In archaea cell walls do not contain peptidoglycan but pseudopeptoglycans, polysaccharides, proteins or glucoproteins.
Eukaryotes
The eukaryotic group has a true nucleus surrounded by a cell membrane and contains genetic material, namely chromosomes which contain DNA and proteins. Eukaryotes have two types of ribosomes namely large ribosomes and small ribosomes. Large ribosomes are found in the cytoplasm and small ribosomes are found in the mitochondria. Mitochondria play a role in the process of respiration. Examples of eukaryotes are animals and plants. Cell walls, vacuoles, and plastids are cells that only plant cells have. The cell wall is the outermost layer composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin. There are plastids that contain a green pigment (chlorophyll) called chloroplasts. Chloroplast is the place where photosynthesis takes place.
Structure, function and mode of reproduction of bacteria
The morphological structure of bacteria consists of a plasma membrane, ribosomes, nucleoid, cell wall, flagellum, pili, glycocalyx and chromosomes (Figure 1). The plasma membrane functions to enclose the cytoplasm. Ribosomes play a role in protein synthesis. The nucleoid is where the cell's DNA is (not enclosed by a membrane). The cell wall is a rigid structure outside the plasma membrane. Flagella are organs used for locomotion. Fimbriae or commonly called pili are structures used for attachment to surfaces. The glycocalyx is the outer layer of many prokaryotes, usually consisting of a capsule or mucus layer. Chromosomes contain the genetic material of bacteria.
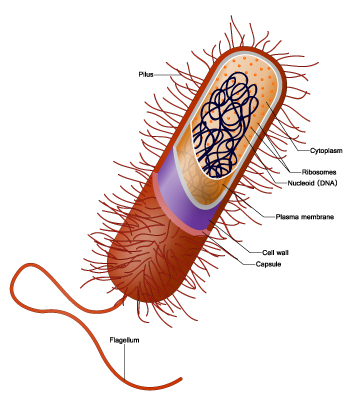
Figure 1 Bacterial cell structure and function
Prokaryotic cells usually have a diameter of 0.5–5µm, much smaller than the diameter of a eukaryotic cell of 10-100 m. Generally, bacterial cells are spherical in diameter about 0.7 – 1.3 m. While the rod-shaped bacterial cells are about 0.2 – 2.0 m wide and 0.7 – 3.7 m long.
The most common bacterial shapes are spherical, rod and spiral (Figure 2). Bacteria that are spherical in shape usually resemble a ball. They can occur singly, in chains of two or more cells, and in clusters resembling bunches of grapes. Rod-shaped bacteria are usually solitary, but in some rods they are arranged in chains. An example of a rod-shaped bacterium is Agrobacterium tumefaciens, the bacterium that causes crown gall disease in woody plants. The spiral-shaped bacteria usually look like a bottle opener. Other spiral bacteria resemble commas or loose coils.
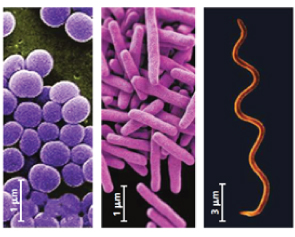
Figure 2 bacterial body shape; (a) round, (b) rod, (c) spiral
Classification of bacteria is divided based on the shape of the body, the position of the flagella in the cells, Gram staining (Gram strain), oxygen requirements and how to obtain food (organic matter). The classification of bacteria based on body shape as previously stated, namely round, rod and spiral. The classification of bacteria based on the position of the flagella is divided into monotric (one flagellum at one end), amphitric (flagellate at each end), lophotric (many flagella at one end), peritrich (many flagella at all sides of the body).
Classification of bacteria based on gram staining is divided into two, namely gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria. Gram-positive bacteria have a simpler cell wall and contain a lot of peptidoglycan. An example of a gram-positive bacterium is the bacterium Clavibacter michiganensis which causes ring rot disease in potatoes. While gram-negative bacteria have a more complex cell wall with less peptidoglycan. An example of gram-negative bacteria is Xanthomonas oryzae which causes crackle disease in rice. Classification of bacteria based on oxygen demand is divided into aerobic bacteria and anaerobic bacteria. Aerobic bacteria are bacteria that require free oxygen to obtain energy. An example of aerobic bacteria is the bacterium Ralstonia solanacearum which causes wilting of tomato plants. While anaerobic bacteria do not need free oxygen to get energy. An example of anaerobic bacteria is the bacterium Pectobacterium carotovorum which causes wet rot in cabbage plants
Classification of bacteria based on how to obtain food (organic matter) is divided into autotrophs and heterotrophs. Autotrophic bacteria are bacteria that make their own food from inorganic materials. Autotroph bacteria, based on their energy source, are divided into: photoautotrophs (energy sources from light) and chemoautotropes (energy sources from chemical reactions). While heterotroph bacteria are bacteria that do not make their own food but utilize finished organic matter derived from other organisms. An example is the saprophytic bacteria that get their food by breaking down the remains of organisms.
Bacterial reproduction is divided into two, namely asexual and sexual. Asexual reproduction of bacteria through binary fission where one bacterial cell will divide into two daughter cells. The process of binary fission begins with the process of DNA replication into two identical copies of DNA, followed by cytoplasmic division and finally a dividing wall is formed between the two bacterial daughter cells.
Sexual reproduction in bacteria is carried out in three ways, namely transformation, transduction and conjugation. Transformation is sexual reproduction by transferring DNA from one bacterium to another directly without a link. Transduction of sexual reproduction by means of DNA transfer assisted by the phage virus as an intermediary. If a bacterium is infected by a phage virus, it will lyse and release the phage and its DNA. The phage virus and DNA then attach to other bacteria. Conjugation is the stage of sexual reproduction in bacteria characterized by the direct transfer of genetic material. The transfer occurs from one bacterium to another via a conjugate bridge.
The role of bacteria in everyday life
Bacteria have both beneficial and harmful roles. In everyday life, we can get many benefits from bacteria. Bacteria play a role in the process of making antibiotics, such as the bacteria Streptomyces griseus which produces streptomycin antibiotics, Streptomyces aureofaciens which produces tetracycline antibiotics, Streptomyces venezuelae which produces chloramphenicol antibiotics, Bacillus polymyxa which produces polymixin antibiotics, Bacillus brevis which produces kerotrisin antibiotics and Bacillus subtilis which produces antibiotics.
Bacteria also play a role in the process of making processed foods such as yogurt, nata decoco and cheese. The yogurt fermentation process uses two types of bacteria, namely Streptococcus thermophilus which plays a role in the formation of yogurt taste and Lactobacillus bulgaricus which plays a role in the formation of aroma. The bacteria that play a role in the process of making nata de coco is the bacterium Acetobacter xylinum. While the bacteria that play a role in the process of making cheese is Lactobacillus bulgaricus.
Bacteria also have a negative role in living things such as humans, animals and plants. As is known bacteria can cause diseases such as diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli bacteria and tuberculosis that attacks the lungs caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria. In animals, the bacterium Bacillus antharicis causes mad cow disease. Besides causing disease in humans and animals, bacteria also cause disease in plants. Xanthomonas oryzae bacteria cause crackle disease in rice and Ralstonia solanacearum bacteria cause wilt in tomato plants.
Reference
Agrios, G.N., 2005. Plant pathology. Elsevier academic press.
Arini, L.D.D., 2017. Utilization of Good Bacteria in Making Fermented Foods That Are Beneficial for Health. Biomedicine, 10(1), pp.1-11.
Reece, J.B., Urry, L.A., Cain, M.L., Wasserman, S.A., Minorsky, P.V. and Jackson, R.B., 2014. Campbell biology (No. s 1309). Boston: Pearson.
Article By: Andika Septiana S, S.P., M.Si
#PTNkeren #DokterTanamanIPB #Bakteri
Source: https://ptn.ipb.ac.id/cms/en/news/detail/259/the-morphological-structure-of-bacteria-and-their-role-in-life
0 Response to "prokaryotes plants palm tree drawings"
Post a Comment